For penetration testing, Hack the box provides us with machines and environment where we can improve our penetration skills. In order to gain access to machines, we need to connect to HTB (Hack the box) through VPN.
Setting up the VPN connection
- So once we have logged to HTB, Click on connect to HTB. Here, select Starting Point and choose OpenVPN as our VPN Client.
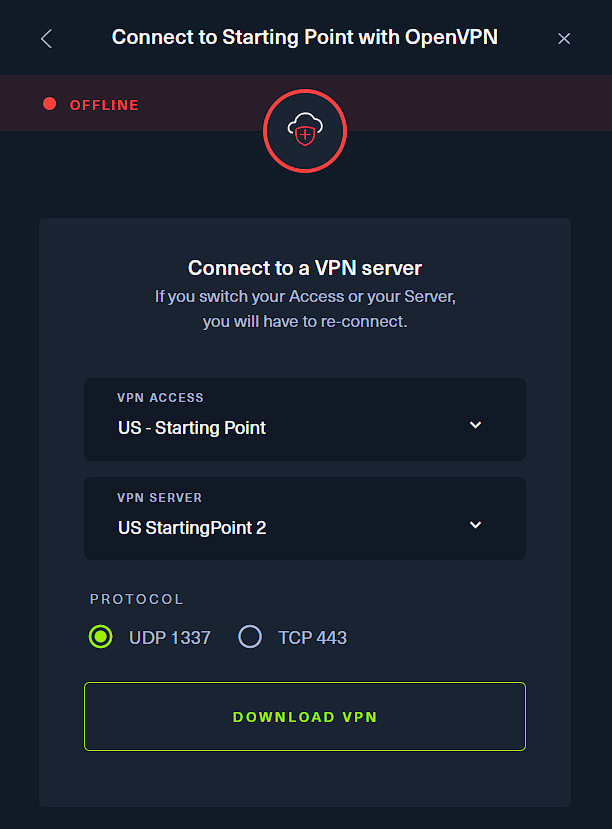
- Select the options as shown in the above image and click on Download VPN
- Locate the folder where the file is downloaded, it will be something like this -
starting\_point\_your\_username.ovpn- this is a OpenVPN configuration file that lets us connect to the VPN server of HTB. - Open the terminal in the directory where the file has been downloaded and type the following command
sudo openvpn starting_point_your_username.ovpn
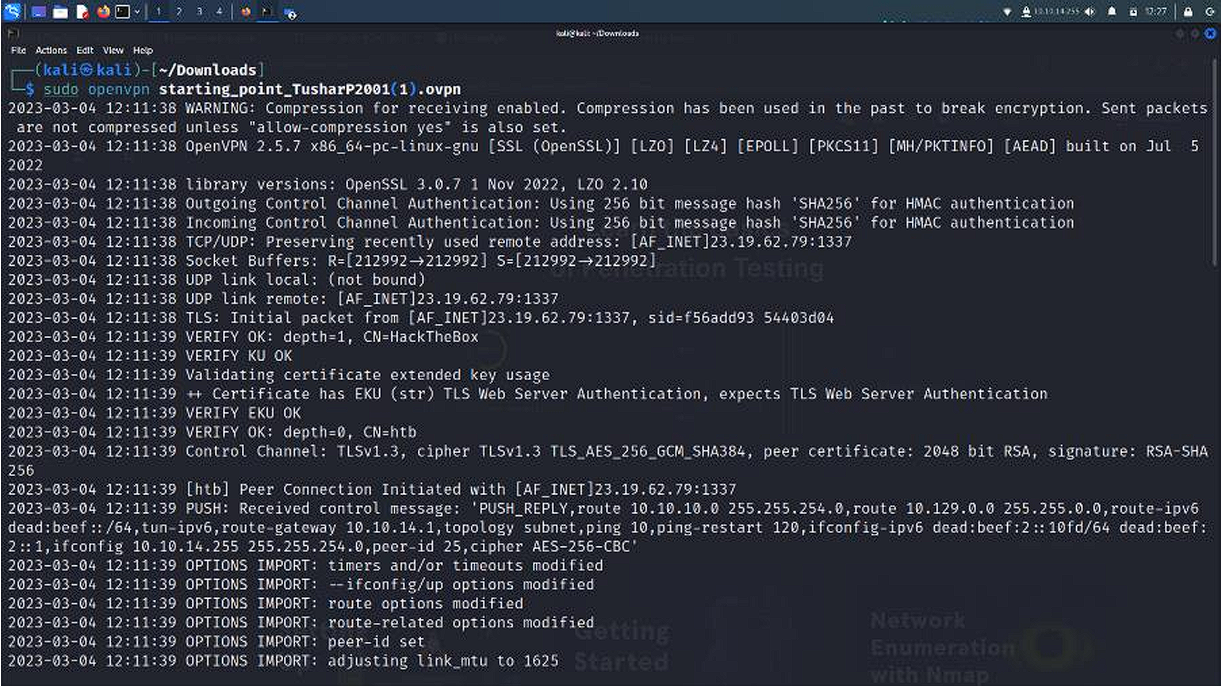
-
Once this command runs, do not close the terminal as this establishes a VPN connection to HTB.
Starting with Machines
Every machine has its own walkthrough and a different set of questions. You need to go through the walkthrough pdf, answer the questions to get to the next levels, find the root flag and submit it to win the machine.
Note
You always need to spawn the machine before beginning, it will connect it to a test server through the VPN connection for your safety. Do not open another machine until you have completed the current one
Meow Machine
- You are provided with a IP address after you spawn the machine. This IP address will be used for further processes hence note it down.
- To see if the target IP address is active, you need to type the following command -
ping target_ip
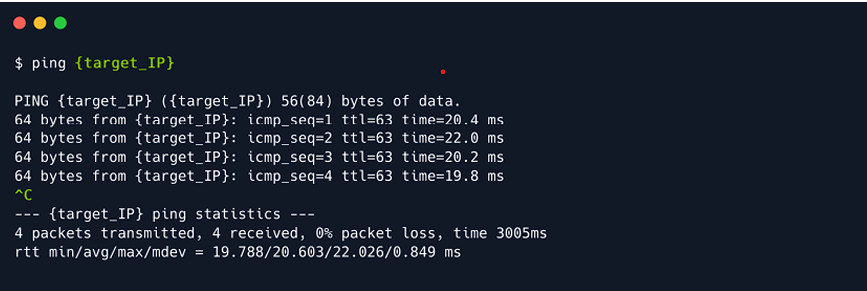
- If you receive the ICMP packets back, the target IP is active
- Do a nmap scan to further analyze the target IP. Type the following cmomand -
sudo nmap -sV target_IP
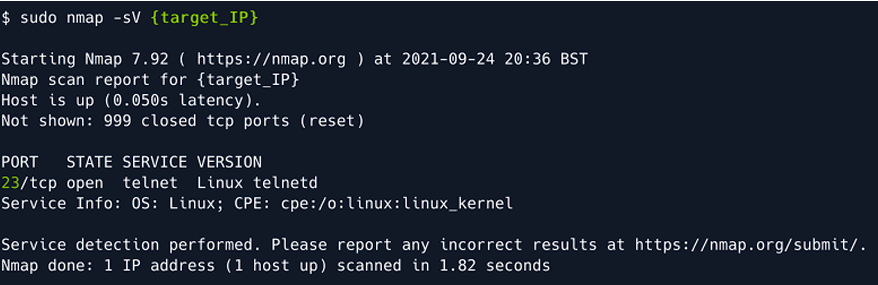
We learnt that the telnet is being use so lets dicsover that. Type the following command to use the telnet service:
telnet target_ip

Some typical important accounts have self-explanatory names, such as:
admin
administrator
root
Try the above names to see if you get the access to the files.
Once you get access to the file directory, type the ls command to list the files in the directory.
Open the file named file.txt to get your root flag.

Enter this root flag id into the box to complete your machine.
Answers of Tasks:
Task 1 : Virtual Machine
Task 2 : terminal
Task 3 : openvpn
Task 4 : tun
Task 5 : ping
Task 6 : nmap
Task 7 : telnet
Task 8 : root
Task 9 : {root flag}
Fawn Machine
This machine is based on the ftp protocol. Lets use the ftp command on our own host. Type the following command to install ftp or to update it.
sudo apt install ftp -y
Use ftp -h to see what it is capable of.
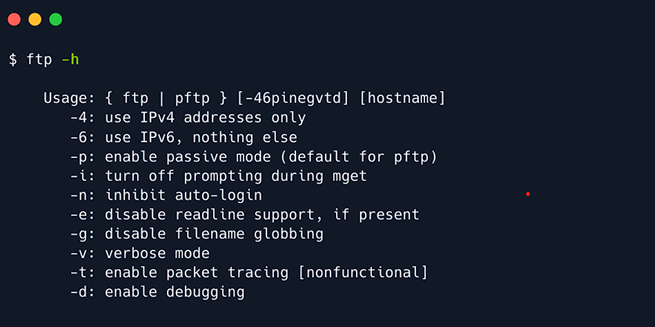
Let us now use ftp on the given target IP. Type the following command:
ftp target_ip
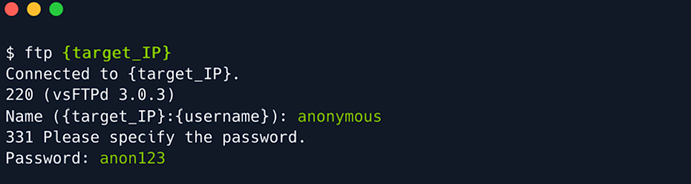
The prompt will ask for a username. The machine is set to have a misconfiguration so that an account named ‘anonymous’ would be able to get into the system.
Once your into the system you can type help to get all the useful commands.
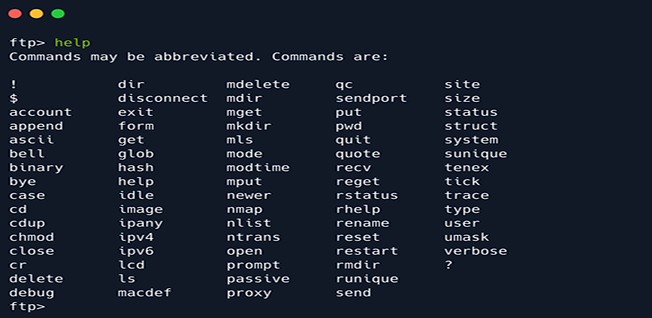
Type ls to list the documents and directories in the system and then use get to retrieve the flag
document.
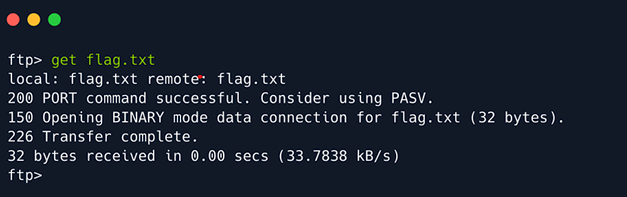
This document will get downloaded in your system after using get. Open the file and type the root flag into the empty field in hackthebox to complete the machine.
Answers of tasks:
Task 1 : File Transfer Protocol
Task 2 : 21
Task 3 : SFTP
Task 4 : ping
Task 5 : vsftpd 3.0.3
Task 6 : unix
Task 7 : ftp -h
Task 8 : anonymous
Task 9 : 230
Task 10 : ls
Task 11 : get
Task 12 : {root flag}
Dancing Machine
In order to successfully enumerate share content on the remote system, we can use a script called smbclient . If the script is not present on your Virtual Machine, you can install it by typing the following command in your terminal (for Debian based operating systems):
sudo apt-get install smbclient
Run the following command to start the smbclient on the target_IP:
smbclient -L target_IP
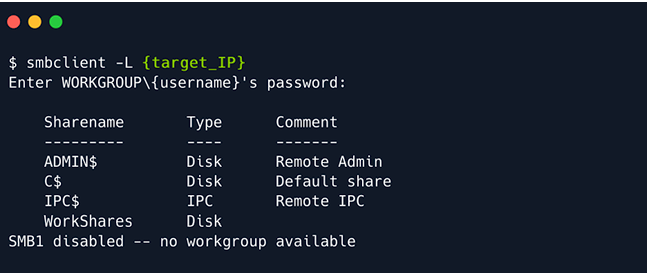
It will ask for a password where you can try the common ones.( such as anonymous, admin, root)
The above command gave us several shares which mean as follows:
ADMIN$ -
Administrative shares are hidden network shares created by the Windows NT family of operating systems that allow system administrators to have remote access to every disk volume on a network-connected system. These shares may not be permanently deleted but may be disabled.
C$ -
Administrative share for the C:\ disk volume. This is where the operating system is hosted.
IPC$ -
The inter-process communication share. Used for inter-process communication via named pipes and is not part of the file system.
WorkShares
Custom share.
Type the following command to try to access these shares
smbclient \\\target_ip\nameOfTheShare
Sometimes the access won’t be provided due to improper credentials.
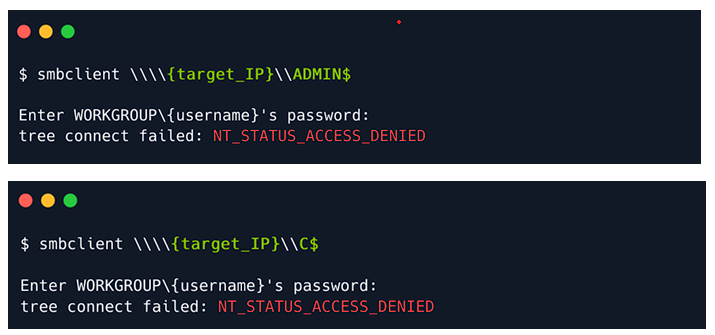
This happens because the above shares that are used in the images are strongly configured. They need proper credentials to get access to. We need to find those shares that are poorly configured.
Same idea here. Last chance. We proceed with attempting to log in to the custom WorkShares SMB share. This seems to be human-made, thus prone to misconfiguration.
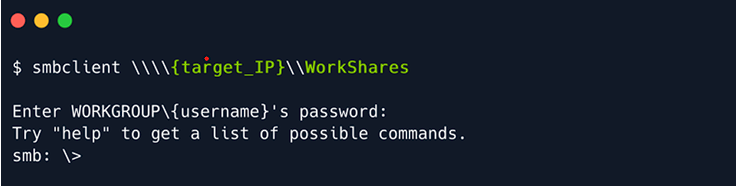
We will be using the following to navigate the share:
ls: listing contents of the directories within the share
cd: changing current directories within the share
get: downloading the contents of the directories within the share
exit: exiting the smb shell
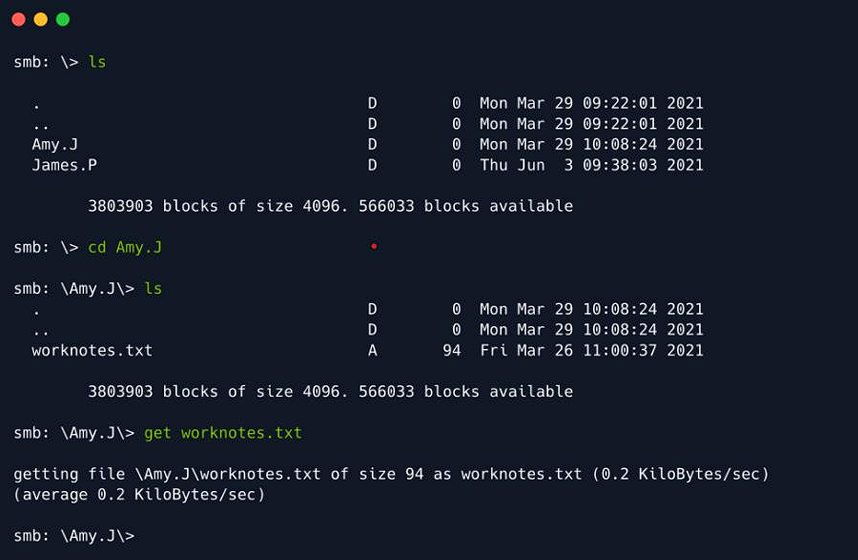
If you do not find the flag.txt file in a directory then navigate to other directory using linux file
system commands then search there.
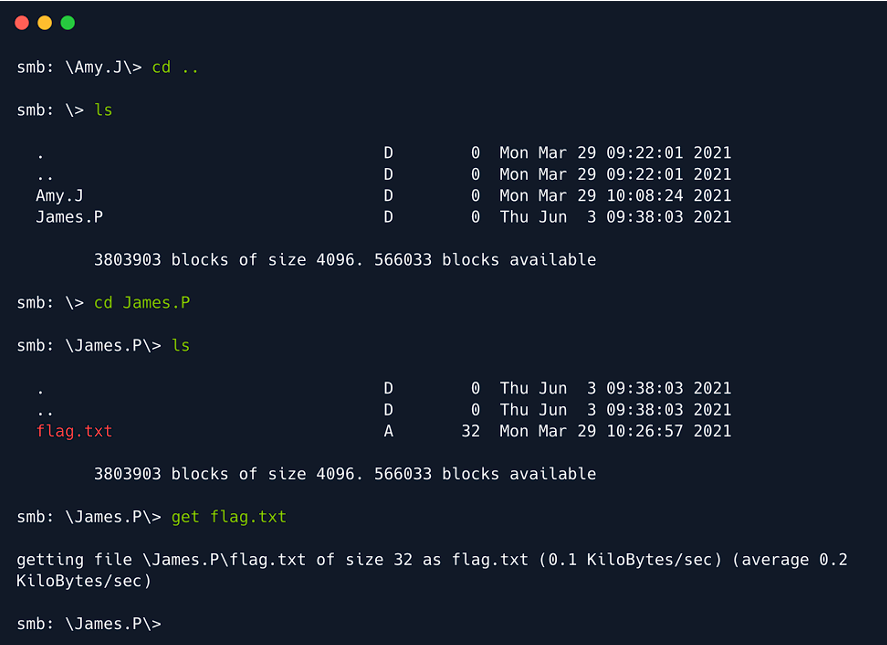
We found the flag.txt in the James.P folder. Download the file using get.
Open the terminal in the folder that contains the flag.txt file. Use cat command to view the file. You will find the root flag value there which needs to be inputted in the text field on the site to complete the machine.
Answers of tasks:
Task 1 : Server Message Block
Task 2 : 445
Task 3 : microsoft-ds
Task 4 : -L
Task 5 : 4
Task 6 : WorkShares
Task 7 : get
Task 8 : {root flag}
Redeemer Machine
In order to verify the connectivity and availability of the target run the ping command.
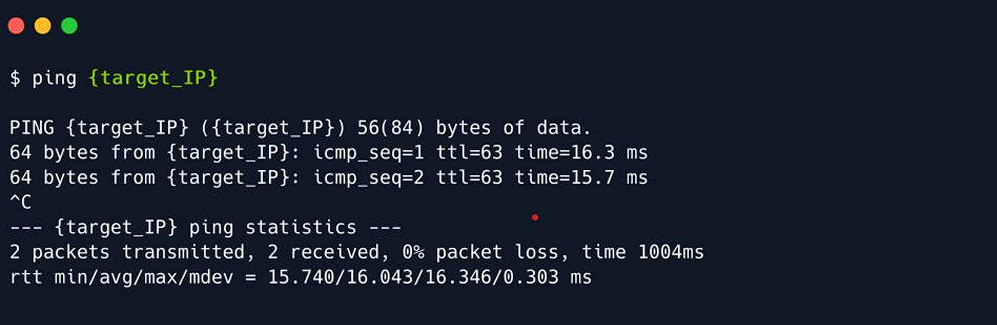
Use nmap to further analyse the target_IP.
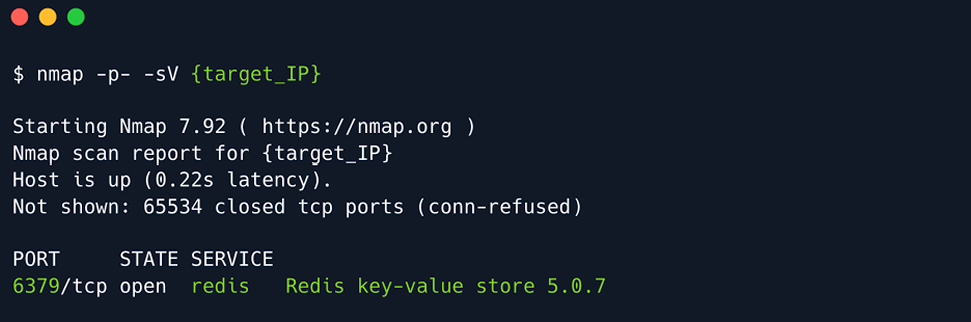
Redis (REmote DIctionary Server) is an open-source advanced NoSQL key-value data store used as a database, cache, and message broker. The data is stored in a dictionary format having key-value pairs. It is typically used for short term storage of data that needs fast retrieval. Redis does backup data to hard drives to provide consistency.
Use the following command to download the redic-cli utility:
sudo apt install redis-tools
redis-cli –help , command will help you understand the several switches and and their
description.
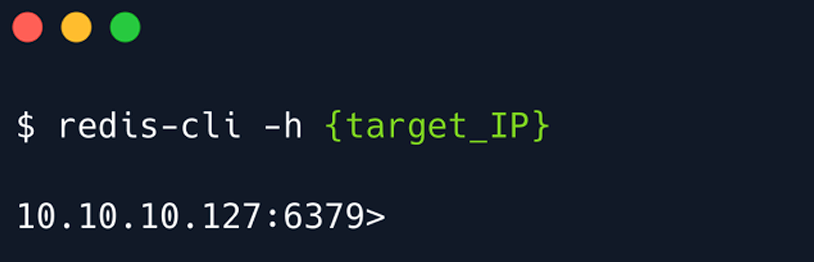
Connect to the redis server by using the following command
redis-cli -h target_ip
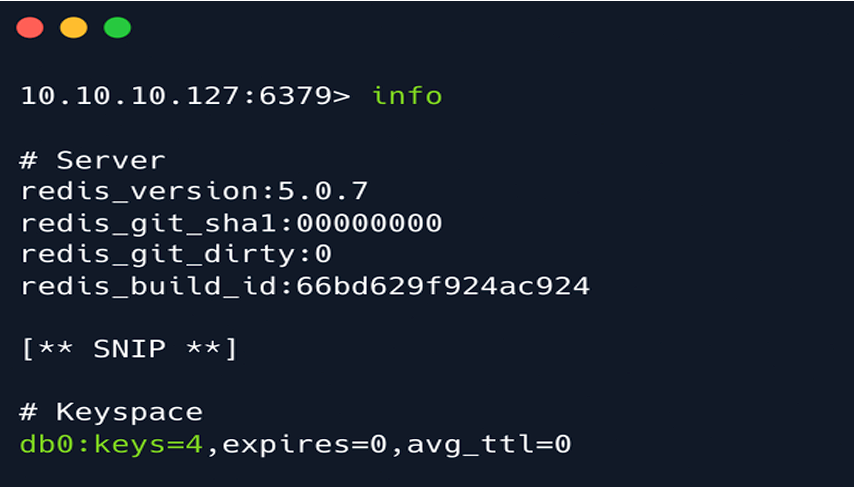
One of the basic Redis enumeration commands is info which returns information and statistics
about the Redis server.
Select the Redis logical database by using the select command followed by the index number of the database that needs to be selected:
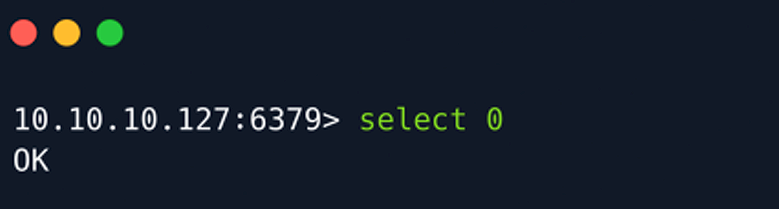
Use the command keys * to list all the keys in the database.
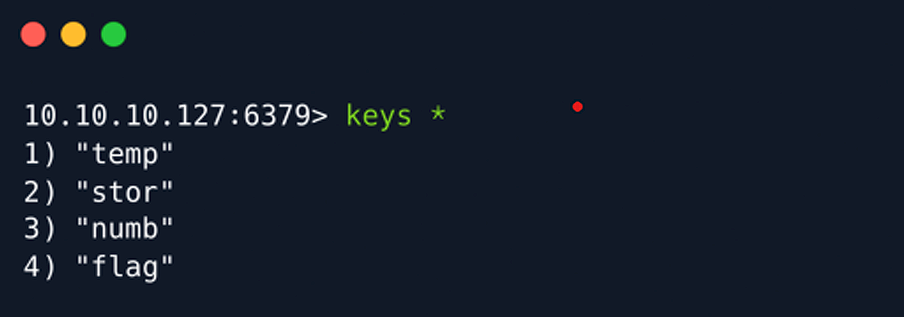
We can view the values stored for a corresponding key using the get command followed by
the keynote.
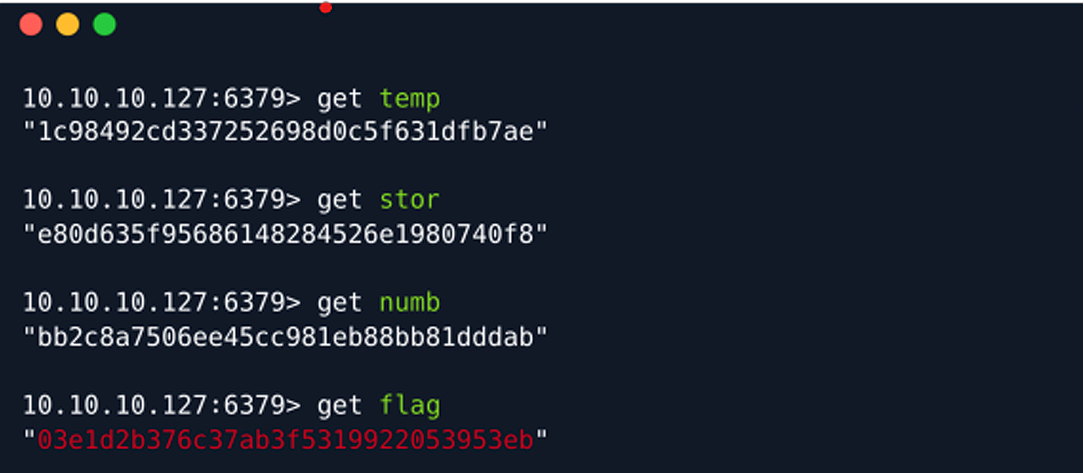
Copy the root flag from the terminal and paste it in the field box of the hackthebox.
You will have completed the machine
Answers of the tasks:
Task 1 : 6379
Task 2 : redis
Task 3 : In-memory Database
Task 4 : redis-cli
Task 5 : -h
Task 6 : info
Task 7 : 5.0.7
Task 8 : select
Task 9 : 4
Task 10 : keys \*
Task 11 : {root\_flag}
